ORDBMS = a relational database that supports some object oriented features.
Table inheritance
Create a table from a (table-)type.
create type person_type as (id integer, firstname text, lastname text);
create table person of person_type;
Create a table inherits from other table.
create table person (id integer, firstname text, lastname text);
create table person_with_dob ( dob date ) inherits (person);
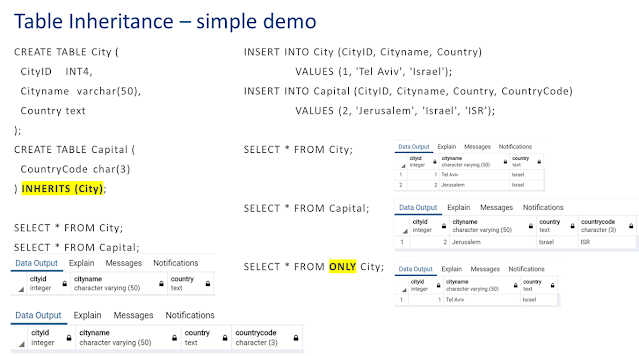
CREATE TABLE City (
CityID INT4,
Cityname varchar(50),
Country text
);
CREATE TABLE Capital (
CountryCode char(3)
) INHERITS (City);
SELECT * FROM City;
SELECT * FROM Capital;
INSERT INTO City (CityID, Cityname, Country)
VALUES (1, 'Tel Aviv', 'Israel');
INSERT INTO Capital (CityID, Cityname, Country, CountryCode)
VALUES (2, 'Jerusalem', 'Israel', 'ISR’);
SELECT * FROM City;
SELECT * FROM Capital;
SELECT * FROM ONLY City;
Definition of methods on the type
create table person (id integer, firstname text, lastname text);
create function fullname(p_row person) returns text
As
$$
select concat_ws(' ', p_row.firstname, p_row.lastname);
$$
language sql;
select p.fullname from person p;
Function overloading
PostgreSQL allows more than one function to have the same name, so long as the arguments are different.
Complex types
Custom data types - Composite Types
PostgreSQL user has the ability to create his own data types based on existing ones (composite types, ranges, arrays, enumerations).
CREATE TYPE inventory_item AS (name text, id integer)
SELECT item.name FROM on_hand WHERE item.price > 9.99;
INSERT INTO mytab (complex_col) VALUES((1.1,2.2));
UPDATE mytab SET complex_col = ROW(1.1,2.2) WHERE ...;
No comments:
Post a Comment