The copy-pastes and explanations blog for SQL code, errors and daily cases! This blog is a 'list' of actions that always good to have available. The copy-paste concept here is short and clear explanations and descriptions (no long stories!) and - of course - the code to take (copy) and use (paste). The blog deals in the database (mostly) and software issues.
Labels
admin
(1)
aix
(1)
alert
(1)
always-on
(2)
Architecture
(1)
aws
(3)
Azure
(1)
backup
(3)
BI-DWH
(10)
Binary
(3)
Boolean
(1)
C#
(1)
cache
(1)
casting
(3)
cdc
(1)
certificate
(1)
checks
(1)
cloud
(3)
cluster
(1)
cmd
(7)
collation
(1)
columns
(1)
compilation
(1)
configurations
(7)
Connection-String
(2)
connections
(6)
constraint
(6)
copypaste
(2)
cpu
(2)
csv
(3)
CTE
(1)
data-types
(1)
datetime
(23)
db
(547)
DB2
(1)
deadlock
(2)
Denali
(7)
device
(6)
dotNet
(5)
dynamicSQL
(11)
email
(5)
encoding
(1)
encryption
(4)
errors
(124)
excel
(1)
ExecutionPlan
(10)
extended events
(1)
files
(7)
FIPS
(1)
foreign key
(1)
fragmentation
(1)
functions
(1)
GCP
(2)
gMSA
(2)
google
(2)
HADR
(1)
hashing
(3)
in-memory
(1)
index
(3)
indexedViews
(2)
insert
(3)
install
(10)
IO
(1)
isql
(6)
javascript
(1)
jobs
(11)
join
(2)
LDAP
(2)
LinkedServers
(8)
Linux
(15)
log
(6)
login
(1)
maintenance
(3)
mariadb
(1)
memory
(4)
merge
(3)
monitoring
(4)
MSA
(2)
mssql
(444)
mssql2005
(5)
mssql2008R2
(20)
mssql2012
(2)
mysql
(36)
MySQL Shell
(5)
network
(1)
NoSQL
(1)
null
(2)
numeric
(9)
object-oriented
(1)
offline
(1)
openssl
(1)
Operating System
(4)
oracle
(7)
ORDBMS
(1)
ordering
(2)
Outer Apply
(1)
Outlook
(1)
page
(1)
parameters
(2)
partition
(1)
password
(1)
Performance
(103)
permissions
(10)
pivot
(3)
PLE
(1)
port
(4)
PostgreSQL
(14)
profiler
(1)
RDS
(3)
read
(1)
Replication
(12)
restore
(4)
root
(1)
RPO
(1)
RTO
(1)
SAP ASE
(48)
SAP RS
(20)
SCC
(4)
scema
(1)
script
(8)
security
(10)
segment
(1)
server
(1)
service broker
(2)
services
(4)
settings
(75)
SQL
(74)
SSAS
(1)
SSIS
(19)
SSL
(8)
SSMS
(4)
SSRS
(6)
storage
(1)
String
(35)
sybase
(57)
telnet
(2)
tempdb
(1)
Theory
(2)
tips
(120)
tools
(3)
training
(1)
transaction
(6)
trigger
(2)
Tuple
(2)
TVP
(1)
unix
(8)
users
(3)
vb.net
(4)
versioning
(1)
windows
(14)
xml
(10)
XSD
(1)
zip
(1)
Columns tables and types
select schema_name(o.schema_id) as SchemaName, object_name(o.object_id) as TableName, c.name as ColumnName, t.name as ColumnType
from sys.columns c
join sys.types t on c.system_type_id = t.system_type_id
join sys.objects o on c.object_id = o.object_id
where c.name = 'SUG-MUTZAR' or c.name = 'STATUS'
order by c.name
Cannot perform alter on a function because it is an incompatible object type
If you have a Multi-Statement Table-Valued Function (MSTVF):
CREATE FUNCTION [DataAccess].[ufn_
( ... )
RETURNS @ret TABLE (ID INT)
AS
BEGIN
...
RETURN
END
If you will try to alter it to – with changing it to an Inline Table-Valued Function:
ALTER FUNCTION [DataAccess].[ufn_
(
@ClientPolTable [DataAccess].[TT_
@SugMimshak INT,
@FromNechonutDate DATETIME = NULL, -- In case no date is selected
@ToNechonutDate DATETIME = NULL
)
RETURNS TABLE AS
RETURN
(
SELECT .....
)
You will be got this error:
Cannot perform alter on 'DataAccess.ufn_
Solution:
You can't alter a function from MSTVF to Inline. So, drop and create again the function.
CREATE FUNCTION [DataAccess].[ufn_
SSIS issue: Decimal fields are imported from csv files without the decimal part
Decimal fields are imported from csv files to the database tables without the decimal part.
(12.547 --> 12.000).
The data imported via SSIS.
This is the definition ion the Flat File Connection Manager:
Solution:
Declare the fields in the Flat File Connection Manager as Numeric, with the correct precision and scale:
Why decimal declaration is not fit to decimal fields? Ask Microsoft :)
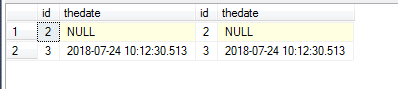
NULL in JOIN
Problem: Join 2 tables, but there are some fit cases with NULL value – and they are not return.
Fast fix: ISNULL in the JOIN.
But, let's take a look to pay attention on this.
create table #aaa (id int, thedate datetime)
create table #bbb (id int, thedate datetime)
insert into #aaa (id, thedate) values (1, '2010-01-01'), (2, NULL), (3, getdate())
insert into #bbb (id, thedate) values (1, '2005-07-01'), (2, NULL), (3, getdate())
-- "equel" nulls will not be return
select *
from #aaa a
join #bbb b on a.id = b.id
and b.thedate = a.thedate
-- only "equel" nulls will be return
select *
from #aaa a
join #bbb b on a.id = b.id
where b.thedate is null
and a.thedate is null
-- all joins will be return
select *
from #aaa a
join #bbb b on a.id = b.id
and isnull(b.thedate, '1900-01-01') = isnull(a.thedate, '1900-01-01')
-- PAY ATTENTION: if the "isnull data" is a possible value in your tables - it can be a problem:
insert into #aaa (id, thedate) values (4, '1900-01-01')
insert into #bbb (id, thedate) values (4, NULL)
select *
from #aaa a
join #bbb b on a.id = b.id
and isnull(b.thedate, '1900-01-01') = isnull(a.thedate, '1900-01-01')
drop table #aaa
drop table #bbb
So:
ISNULL(AAA, GETDATE) can't be a 100% solution to join on datetime,
ISNULL on numeric columns MUST take into consideration which value will be in the ISNULL (common mistake is to put zero – it's a valid numeric value!!!),
ISNULL(AAA, N'') can't be a 100% solution to join on strings (empty string it's a valid numeric value!!!),
And so on...
Remove leading zero's
declare @aaa nvarchar(50) = N'00000100200'
SELECT SUBSTRING(@aaa , PATINDEX('%[^0]%', @aaa), LEN(@aaa ))
Get job step(s) history
select j.name as JobName, s.step_id as Step, s.step_name as StepName,
msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_
((run_duration/10000*3600 + (run_duration/100)%100*60 + run_duration%100 + 31 ) / 60) as RunDurationMinutes
From msdb.dbo.sysjobs j
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps s ON j.job_id = s.job_id
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory h ON s.job_id = h.job_id
WHERE j.[enabled] = 1 -- Only Enabled Jobs
AND j.name = 'YourJobName' -- specific job
AND h.run_status = 1 -- 0=Failed, 1=Succeeded, 2=Retry, 3=Cancelled, 4=In Progress
AND s.step_id = 3 -- specific step
ORDER BY j.name, msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_
[SSISDB].[catalog].[set_object_parameter_value] Cannot find the parameter because it does not exist
What I tried to do:
Sets the value of a parameter in the Integration Services catalog.
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[set_
@object_type=20,
@parameter_name=N'
@object_name=N'MyProcess',
@folder_name= N'MyProcess',
@project_name= N'MyProcess',
@value_type=R,
@parameter_value= N'MyServerName';
GO
Error message:
[SSISDB].[catalog].[set_
Cause and Fix:
Lowercase / Uppercase of the names – environment VS SSIS parameters.
When I set the letters to be exactly the same – it worked.
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[set_
@object_type=20,
@parameter_name= N'MYSERVERNAME',
@object_name=N'MyProcess',
@folder_name= N'MyProcess',
@project_name= N'MyProcess',
@value_type=R,
@parameter_value= N'MYSERVERNAME';
GO
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)