The copy-pastes and explanations blog for SQL code, errors and daily cases! This blog is a 'list' of actions that always good to have available. The copy-paste concept here is short and clear explanations and descriptions (no long stories!) and - of course - the code to take (copy) and use (paste). The blog deals in the database (mostly) and software issues.
Labels
Row counts in all tables
SQL - select dates list between dates
@StartDate DATETIME, -- date and time
@Duration INT,
@ToDate DATETIME;
@Duration = 60,
@ToDate = '2021-08-03 08:00:00.000';
DECLARE @l_Date DATETIME;
SET @l_Date = CAST (@StartDate AS DATE);
; WITH GetDates AS
(
SELECT @StartDate AS OccupiedDate, @l_Date AS CalDate
UNION ALL
SELECT DATEADD(HOUR ,24, OccupiedDate) AS OccupiedDate, DATEADD(HOUR ,24, CalDate) AS CalDate
FROM GetDates
WHERE OccupiedDate < @ToDate
)
SELECT * FROM GetDates;
; WITH GetDates AS
(
SELECT @l_Date AS CalDate
UNION ALL
SELECT DATEADD(HOUR ,24, CalDate) AS CalDate
FROM GetDates
WHERE DATEADD(HOUR ,24, CalDate) < @ToDate
)
SELECT * FROM GetDates;
MySQL Cluster Overview
MySQL Cluster Overview
In MySQL Cluster, there is typically no replication of data. It has only data node synchronization
MySQL Cluster is a shared-nothing architecture
- As a result, no two components of the cluster will share the same hardware.
- The cluster will be fully operational when at least one node is upon each data node group. As a result, the MySQL cluster avoids single point failure and ensures 99.99% availability.
Replication <--> Cluster
Replication
- Master-Slave, one server is designated to act as the master.
- (there is also master-master configuration).
- Asynchronous - not all nodes have the freshest data at all time
- No automatic failover
Cluster
- Internally, the MySQL Cluster also uses synchronous replication.
Replication | Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
Asynchronous / synchronous | Asynchronous | synchronous |
| Automatic failover | No (a slave has to be promoted to master) | Yes |
Downtime when a master fails | Yes | No |
MySQL InnoDB Cluster
MySQL InnoDB Cluster provides high-availability and scaling features.
MySQL InnoDB Cluster consists of at least three MySQL Server instances.
MySQL InnoDB Cluster usually runs in a single-primary mode, with one primary instance (read-write) and multiple secondary instances (read-only).
- Table creation and data insertion can be done only on the primary instance.
- (Advanced users can also take advantage of a multi-primary mode, where all instances are primaries. This is not the common case).
MySQL InnoDB Cluster data nodes are actually a Group Replication.
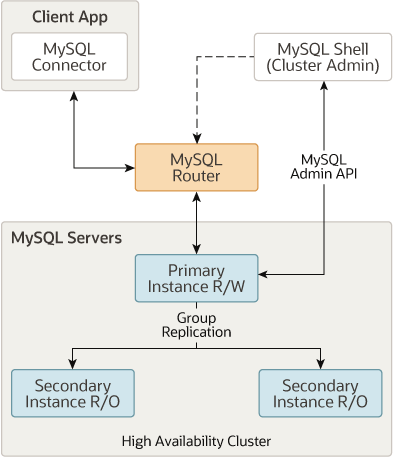
InnoDB Cluster does not provide support for MySQL NDB Cluster.
MySQL NDB Cluster
A standard MySQL server does not support the MySQL Cluster engine NDB.
- MySQL Cluster is tightly linked to the MySQL server, yet it’s a separate product.
- This means we need to install the custom SQL server packaged.
MySQL Galera Cluster
- Galera Cluster for MySQL is a true Multi-Master Cluster based on synchronous replication.
- It is a multi-master database cluster that supports synchronous replication
- https://galeracluster.com/
Different MySQL versions on the same Windows server
Linux
We can only have one version of MySQL setup on the machine using the default installation procedure with apt-get.
If we try to install one version over another, it will replace the first version and will retain the second version.
Windows
In Windows, we can install different MySQL versions on the same server using the installer:
- Install the first instance.
Download MySQL Installer for windows and run it.
- Check and install requirements for MySQL products, Install MySQL, Configure MySQL Server, Set password for root account, (create another user), Create a service for MySQL Server, Apply configuration (= execution of all the above), Finish.
- Run MySQL Installer again, Press “Add” button and you will get all MySQL products list.
- Choose the MySQL version you need and move it to “Products to be installed” list.
- “Next” and move to other steps that similar to the regular installation: Check and install requirements, Download, Installation.
- After installation is finished, “Next” to configuration or if there is no “Next”, Select this version in the installation list and press “Reconfigure”.
- Configure MySQL Server: Set password for root account, (create another user), Create a service for MySQL Server, Apply configuration.
- Finish.
- Checks:
- The "C:\Program Files\MySQL" folder will have two “MySQL Server x.x” folders - one for each version.
- The " C:\ProgramData\MySQL " folder will have two data folders - one for each version.
- MySQL service should be created for each version.
- Enable Remote connection.
Multiple MySQL instances on one server
Notes:
- The process described here is for Linux OS.
- We can only have one version of MySQL setup on the machine using default installation procedure with apt-get.
- If we try to install one version over other, it will replace the first version and will retain the second version.
1. Create Data directory
1.1 Create a directory
mkdir -p /opt/second_server_data/ |
1.2 Initializing the directory
Initializing the directory
chmod --reference /var/lib/mysql /opt/second_server_data/chown --reference /var/lib/mysql /opt/second_server_data/ |
Add rules to the policy file to stop the OS from restricting MySQL to access our newly created directoriesy, etc.
Edit “/etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld”, add these permissions (as the default data dir has).
sudo nano /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqldUnder “# Allow data dir access”:/opt/second_server_data/ r,/opt/second_server_data/** rwk,Under “# Allow pid, socket, socket lock file access”:/var/run/mysqld/second_server.pid rw,/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock rw,/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock.lock rw,/run/mysqld/second_server.pid rw,/run/mysqld/second_server.sock rw,/run/mysqld/second_server.sock.lock rw, |
Restart apparmor service
(AppArmor is a linux kernel security module that allows you to restrict program capabilities on a per-program basis)
sudo service apparmor restart |
1.3 Initialize the created data dir as a MySQL data directory
mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/ |
Check the contents of the dir: “sudo ls -l /opt/second_server_data/”.
These files should be there (drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql …..) : mysql, performance_schema, sys
A default root password was generated and stored in “/var/log/mysql/error.log”
2020-12-17T08:45:06.170673Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: 1hfBQ5G66d_V

2. Create a socket (and a TCP port) for a client
Given correct permissions MySQL is able to create these on its own.
3. MySQL configurations
* Steps 3-5 can be done also using mysqld or mysqld_safe.
start mysqld / mysqld_safe
sudo mysqld --no-defaults --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/ --port=3307 --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock |
- no-defaults: Makes sure no options are loaded from option files.
- data-dir: Path to the data directory that we created.
- port: TCP port.
- mysqlx: X plugin is an interface to allow MySQL function as a document store. Since we don’t need it, we will disable it.
- socket: Specify location of socket file

sudo mysqld_safe --no-defaults --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/ --port=3307 --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock |
4. Testing
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3307 -u root –p--Ormysql --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock -u root –p--Stop mysqld_safe using:sudo mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3307 -u root -p shutdown |
In order to perform SQL operations, the auto generated password should be changed:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'second_server'; |

5. Create cnf file for the second instance
5.1 Copy the cnf file and add to it:
[mysqld]server-id = 2port = 3307socket = /var/run/mysqld/second_server.sockdatadir = /opt/second_server_data/#mysqlx = 0 |
or
[mysqld_safe]server-id = 2port = 3307socket = /var/run/mysqld/second_server.sockdatadir = /opt/second_server_data/#mysqlx = 0 |
5.2 start mysqld/mysqld_safe with the new cnf
sudo mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnf |
or
sudo mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnf |
5.3 Testing as before
6. Create a service for the new instance
Create a service using system
6.1 Create “.service” file
Save in “/lib/systemd/system/” or “/etc/systemd/system”
touch mysql_3307.servicevi mysql_3307.service[Unit]Description=MySQL 3307 serviceAfter=network.target[Service]Type=simpleRestart=alwaysUser=mysqlGroup=mysqlExecStart=/etc/mysql/sudo mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnfTimeoutSec=600RuntimeDirectory=mysqldRuntimeDirectoryMode=755LimitNOFILE=5000[Install]WantedBy=multi-user.target |
6.2 Start the service
Sudo systemctl start mysql_3307 |
6.3 Checking
systemctl status mysql_3307journalctl -xe |
6.* Stop the service (if required)
systemctl stop mysql_3307 |
