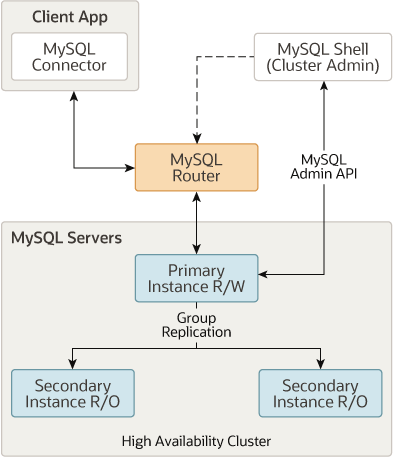
Notes:
- The process described here is for Linux OS.
- We can only have one version of MySQL setup on the machine using default installation procedure with apt-get.
- If we try to install one version over other, it will replace the first version and will retain the second version.
1. Create Data directory
1.1 Create a directory
mkdir -p /opt/second_server_data/
|
1.2 Initializing the directory
Initializing the directory
chmod --reference /var/lib/mysql /opt/second_server_data/
chown --reference /var/lib/mysql /opt/second_server_data/
|
Add rules to the policy file to stop the OS from restricting MySQL to access our newly created directoriesy, etc.
Edit “/etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld”, add these permissions (as the default data dir has).
sudo nano /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld
Under “# Allow data dir access”:
/opt/second_server_data/ r,
/opt/second_server_data/** rwk,
Under “# Allow pid, socket, socket lock file access”:
/var/run/mysqld/second_server.pid rw,
/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock rw,
/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock.lock rw,
/run/mysqld/second_server.pid rw,
/run/mysqld/second_server.sock rw,
/run/mysqld/second_server.sock.lock rw,
|
Restart apparmor service
(AppArmor is a linux kernel security module that allows you to restrict program capabilities on a per-program basis)
sudo service apparmor restart
|
1.3 Initialize the created data dir as a MySQL data directory
mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/
|
Check the contents of the dir: “sudo ls -l /opt/second_server_data/”.
These files should be there (drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql …..) : mysql, performance_schema, sys
A default root password was generated and stored in “/var/log/mysql/error.log”
2020-12-17T08:45:06.170673Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: 1hfBQ5G66d_V

2. Create a socket (and a TCP port) for a client
Given correct permissions MySQL is able to create these on its own.
3. MySQL configurations
* Steps 3-5 can be done also using mysqld or mysqld_safe.
start mysqld / mysqld_safe
sudo mysqld --no-defaults --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/ --port=3307 --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock
|
- no-defaults: Makes sure no options are loaded from option files.
- data-dir: Path to the data directory that we created.
- port: TCP port.
- mysqlx: X plugin is an interface to allow MySQL function as a document store. Since we don’t need it, we will disable it.
- socket: Specify location of socket file

sudo mysqld_safe --no-defaults --datadir=/opt/second_server_data/ --port=3307 --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock
|
4. Testing
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3307 -u root –p
--Or
mysql --socket=/var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock -u root –p
--Stop mysqld_safe using:
sudo mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3307 -u root -p shutdown
|
In order to perform SQL operations, the auto generated password should be changed:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'second_server';
|

5. Create cnf file for the second instance
5.1 Copy the cnf file and add to it:
[mysqld]
server-id = 2
port = 3307
socket = /var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock
datadir = /opt/second_server_data/
#mysqlx = 0
|
or
[mysqld_safe]
server-id = 2
port = 3307
socket = /var/run/mysqld/second_server.sock
datadir = /opt/second_server_data/
#mysqlx = 0
|
5.2 start mysqld/mysqld_safe with the new cnf
sudo mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnf
|
or
sudo mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnf
|
5.3 Testing as before
6. Create a service for the new instance
Create a service using system
6.1 Create “.service” file
Save in “/lib/systemd/system/” or “/etc/systemd/system”
touch mysql_3307.service
vi mysql_3307.service
[Unit]
Description=MySQL 3307 service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
User=mysql
Group=mysql
ExecStart=/etc/mysql/sudo mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/second_server.cnf
TimeoutSec=600
RuntimeDirectory=mysqld
RuntimeDirectoryMode=755
LimitNOFILE=5000
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
6.2 Start the service
Sudo systemctl start mysql_3307
|
6.3 Checking
systemctl status mysql_3307
journalctl -xe
|
6.* Stop the service (if required)
systemctl stop mysql_3307
|